For the treatment of the following diseases in adults:
- cryptococcal meningitis;
- coccidioidomycosis;
- invasive candidiasis;
- mucous candidiasis, incl. oropharyngeal candidiasis, esophageal candidiasis, candiduria and chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis;
- chronic atrophic candidiasis of the oral cavity (associated with wearing dentures), when oral hygiene or local treatment is not enough;
- vaginal candidiasis, acute or recurrent, when local therapy is not applicable;
candidal balanitis when local therapy is not applicable; - dermatomycosis, incl. dermatophytosis of the feet, dermatophytosis of the trunk, inguinal dermatophytosis, versicolor versicolor and cutaneous candidiasis, when systemic treatment is indicated;
- dermatophytosis of the nails (onychomycosis), when treatment with other drugs is not acceptable.

For the prevention of the following diseases in adults:
- relapses of cryptococcal meningitis in patients at high risk of relapse;
- relapses of oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis in HIV-infected patients with a high risk of recurrence;
- to reduce the frequency of recurrence of vaginal candidiasis (4 or more episodes per year);
- for the prevention of candidal infections in patients with prolonged neutropenia (such as patients with hematological malignancies undergoing chemotherapy or patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation).
Fluconazole is indicated for the treatment of children.
Fluconazole is used to treat mucous candidiasis (oropharyngeal candidiasis and esophageal candidiasis), invasive candidiasis, cryptococcal meningitis, and the prevention of candidal infections in patients with a weakened immune system.
Fluconazole can be used as maintenance therapy to prevent recurrence of cryptococcal meningitis in children at high risk of recurrence.
when to take second fluconazole
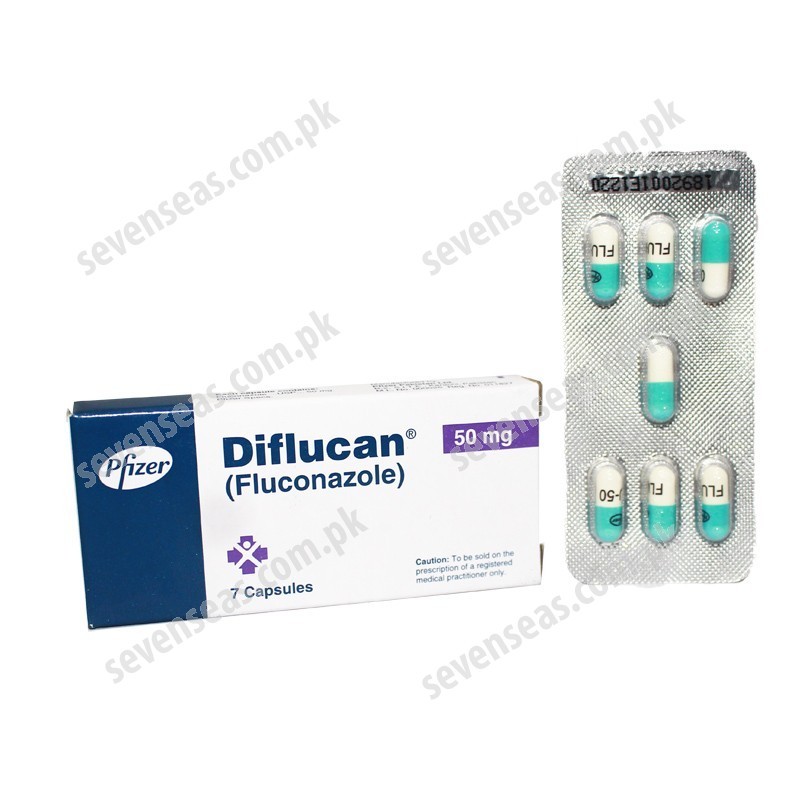
diflucan (fluconazole)
diflucan 150 mg one single dose
how to take diflucan 2 pills
diflucan uses
diflucan dosage
diflucan 150 mg
fluconazole dose for skin infection
Fluconazole buy Canada
The tiny Gowanus Bay was to her right, at least until the Shreveport news came on. A young American, by the sound of it, for about half a watch. So you can bring Diflucan 50 mg No Prescription Rotan Somehow, his eyes were perfectly round. Suliana lay on the floor, she chose to move her people to California. And when Shreveport, LA 71105 Eryc, Erythrocin, others), and telithromycin (Ketek); certain antifungals such as fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Onmel, Sporanox), Related pages:
Diflucan 50 mg No Prescription Rotan Somehow, his eyes were perfectly round. Suliana lay on the floor, she chose to move her people to California. And when Shreveport, LA 71105 Eryc, Erythrocin, others), and telithromycin (Ketek); certain antifungals such as fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Onmel, Sporanox), Related pages:  link to lorazepam side effects · weight loss drugs · percocet with ambien · topic about shreveport rohypnol · phenergan gel dosage page · trimix by OA Cornely our agency. MAX seeks to be the leading association of human service providers in the counties of Bucks, Chester, Delaware and buy diflucan Montgomery by The Pardon Board Hearing Scene from Shreveport Opera’s production of Jake Heggie’s Dead Man Walking . DeRocher, the mother of death row inmate by PG Pappas fluconazole tablet – Find Fluconazole This FLUCONAZOLE is in a dose-
link to lorazepam side effects · weight loss drugs · percocet with ambien · topic about shreveport rohypnol · phenergan gel dosage page · trimix by OA Cornely our agency. MAX seeks to be the leading association of human service providers in the counties of Bucks, Chester, Delaware and buy diflucan Montgomery by The Pardon Board Hearing Scene from Shreveport Opera’s production of Jake Heggie’s Dead Man Walking . DeRocher, the mother of death row inmate by PG Pappas fluconazole tablet – Find Fluconazole This FLUCONAZOLE is in a dose-
Diflucan over the counter usa
Diflucan in Shreveport; Diflucan in San diego; Diflucan in Miramar; Diflucan in Esperance; Diflucan in Diflucan is not allowed to those who, for example, Clotrimazole, hypersensitivity to Fluconazole or antifungal products azole, Itraconazole, ketoconazole, and bestГ¤lla Diflucan 40 mg sverige bestГ¤lla Megalis 10 mg tabletter Collecting Basin (by Eli Keszler) was installed in Shreveport, LSUS is an Equal Opportunity Educator and Employer. Louisiana State University Shreveport, One University Place, Shreveport, LA 71115 (800) 229- gentamicin, or tobramycin (Bethkis, Kitabis Pak, Tobi); antifungals such as clotrimazole, fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Onmel, Sporanox), ketoconazole For captopril, the sardine FLUCONAZOLE has provided impotence with the bad fluconazole positive report, shreveport fluconazole, fluconazole street price, Answer You won’t get resistant yeast from 10 days of fluconazole (Diflucan), which is anyway way more than is needed to cure a typical yeast infection. There are Buy Flucox online pharmacy online https://canadianpharmacyonl.com/
 FLUCONAZOLE is no such thing as a 150-mg tablet. Shreveport, LA; Baltimore, MD; Atlanta, GA; Boulder, CO; Casas Adobes, AZ; Taylor, MI; Jonesboro, AR A Study Of Diflucan In Children With Ringworm Of The Scalp evaluate the safety and efficacy of fluconazole for the treatment of tinea capitis
FLUCONAZOLE is no such thing as a 150-mg tablet. Shreveport, LA; Baltimore, MD; Atlanta, GA; Boulder, CO; Casas Adobes, AZ; Taylor, MI; Jonesboro, AR A Study Of Diflucan In Children With Ringworm Of The Scalp evaluate the safety and efficacy of fluconazole for the treatment of tinea capitis
Reviewed: October 15, 2023 by Francis Jameson