Hair Loss and Its Impact on Men
Hair loss, medically known as androgenetic alopecia, affects millions of men worldwide. It is a condition that can strike at any age, although it commonly begins in a man’s 20s or 30s, progressing as they age. The receding hairline, thinning crown, or gradual baldness isn’t just a cosmetic issue—it often leaves deep psychological scars. Hair is closely tied to one’s identity and self-image, and for many men, losing hair means a loss of confidence, youthfulness, and social attractiveness.

While hair loss is largely determined by genetics, environmental factors, stress, and health conditions can also accelerate the process. Androgenetic alopecia, the most common form of hair loss, is characterized by the miniaturization of hair follicles due to the action of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. The shrinking hair follicles eventually stop producing hair altogether, resulting in thinning and bald patches.
Historically, men resorted to wearing wigs, using hairpieces, or accepting the hair loss as inevitable. However, advancements in medical research over the past few decades have led to treatments that can slow, stop, or even reverse hair loss. Among these treatments, one of the most notable is Proscar, known for its active ingredient finasteride.

Although initially developed for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), Proscar was discovered to have a surprising side effect—hair regrowth. Finasteride, at lower doses, was eventually repurposed and marketed as Propecia, a medication specifically aimed at treating male pattern baldness. Today, Proscar is often used off-label for hair loss, with men seeking affordable and accessible ways to regain their hair and confidence.
What is Proscar (Finasteride)?
Proscar is a medication that contains finasteride, a drug originally approved by the FDA in 1992 for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition where the prostate gland becomes enlarged and affects urinary function in older men. Manufactured by Merck & Co., Proscar is prescribed at a dose of 5 mg daily to reduce the size of the prostate by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).

DHT is responsible for prostate growth, but it is also implicated in hair loss. It wasn’t long after Proscar was introduced that doctors and researchers noticed an interesting side effect in men taking the drug for prostate issues—those with androgenetic alopecia saw improvements in their hair. This discovery led to the development of Propecia, a lower-dose version of finasteride (1 mg) specifically designed to treat male pattern baldness.
While Propecia is the go-to medication for hair loss, many men opt to use Proscar off-label for the same purpose. Proscar contains a higher dose of finasteride (5 mg), and patients may split the tablet to match the 1 mg dosage recommended for hair loss. This practice is common because Proscar is often more affordable and accessible, but it should always be done under a doctor’s supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Why is Proscar Used Off-Label for Hair Loss? Men choose Proscar for several reasons:
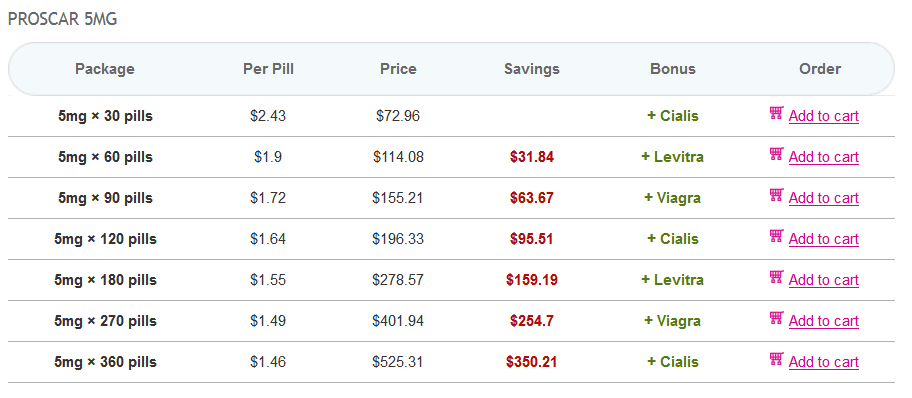
- Cost-Effectiveness: In many cases, Proscar is less expensive than Propecia, and patients can split the 5 mg tablets into smaller doses to treat hair loss.
- Widespread Availability: Since Proscar is prescribed for BPH, it is widely available in pharmacies, making it an accessible option for hair loss sufferers.
- Identical Active Ingredient: Proscar and Propecia both contain finasteride, meaning they have the same mechanism of action. The only difference is the dosage, with Proscar containing a higher concentration.
Despite these advantages, it is crucial to follow medical advice when using Proscar for hair loss, as there are risks associated with improper dosing and long-term use.
How Proscar Works for Hair Loss
The success of Proscar in treating hair loss lies in its ability to combat dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a potent androgen hormone derived from testosterone. DHT plays a critical role in the development of male characteristics, but it also contributes to hair loss in men with a genetic predisposition to androgenetic alopecia.

DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, particularly in areas like the scalp, and causes the hair follicles to shrink—a process known as miniaturization. Over time, the affected hair follicles produce thinner, shorter hairs until they eventually stop producing hair altogether. This leads to the characteristic patterns of hair thinning and baldness seen in male pattern baldness.
Finasteride, the active ingredient in Proscar, works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. This enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. By blocking the formation of DHT, finasteride reduces the levels of DHT in the scalp, which in turn slows or even reverses the miniaturization process of hair follicles. In essence, Proscar allows hair follicles to recover and resume their normal hair-producing function.
Timeline for Hair Regrowth When it comes to treating hair loss with Proscar, patience is key. Unlike some hair loss treatments that may offer faster, albeit temporary, results (like topical minoxidil), finasteride works gradually to combat hair thinning and baldness.

- First 3 Months: During the first few months of treatment, patients may not notice significant changes in hair growth. In fact, some may experience shedding, where hair temporarily falls out as weaker hairs make way for new, stronger hairs. This can be alarming but is a sign that the treatment is working.
- 6 to 12 Months: Around the six-month mark, many men begin to see tangible results. Hair loss typically stabilizes, meaning that the rapid thinning or shedding that was occurring before treatment slows down or stops altogether. Some patients may start to see signs of new hair growth, particularly in areas like the crown.
- 12 to 24 Months: Significant hair regrowth is often observed after one year of consistent treatment. For some men, hair density improves, and the overall appearance of the hairline or thinning areas is noticeably better. Continuing the treatment beyond 12 months can lead to further improvements.
Finasteride, however, is not a cure for hair loss. The effects are only maintained as long as the medication is taken. If treatment is discontinued, DHT levels rise again, leading to the resumption of hair loss within a few months.
Clinical Evidence: Effectiveness of Proscar in Treating Hair Loss
The effectiveness of finasteride, both in the forms of Proscar and Propecia, has been extensively studied in clinical trials and real-world settings. Numerous studies have demonstrated that finasteride is highly effective in halting hair loss and promoting regrowth in men suffering from androgenetic alopecia.

One of the most significant clinical trials on the subject was conducted by Merck, the manufacturer of Propecia. In this study, over 1,500 men with mild to moderate hair loss were treated with either finasteride (1 mg) or a placebo for two years. The results were compelling:
- 90% of men treated with finasteride either experienced a halt in hair loss or regrowth of hair.
- 66% of men showed visible improvements in hair count and density after two years of treatment.
- Men who took finasteride reported significantly higher satisfaction with their hair appearance compared to the placebo group.
Long-Term Results
The benefits of finasteride extend beyond the first year of use. Studies that followed patients for up to five years revealed that the drug continued to prevent hair loss and promote regrowth over long periods. In a five-year study, men who consistently used finasteride maintained their hair density and had less hair thinning compared to men who stopped treatment or were on a placebo.
Success Rates by Age and Hair Loss Stage
Finasteride tends to be most effective in younger men or those in the early stages of hair loss. Men in their 20s and 30s, who start treatment before significant hair thinning or balding occurs, are more likely to experience better regrowth outcomes than those who begin treatment later in life. However, men in their 40s and 50s also benefit from finasteride, especially when used to halt further hair loss.
Proscar vs. Propecia
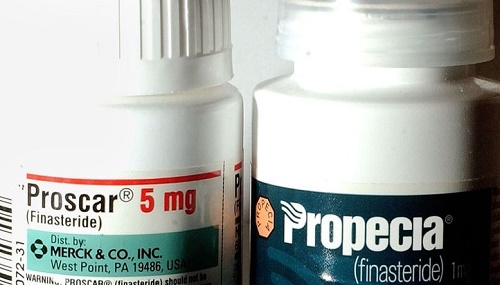
While Proscar (5 mg finasteride) is primarily marketed for treating BPH, its effectiveness for hair loss is identical to that of Propecia (1 mg finasteride). The primary difference is dosage. Many men use Proscar off-label for hair loss because it is more affordable or easier to obtain. However, splitting Proscar tablets to achieve the correct dosage for hair loss treatment (1 mg) must be done carefully, and it is best to follow a doctor’s guidance.
Proscar Administration for Hair Loss
When using Proscar for hair loss, the recommended daily dosage is 1 mg of finasteride. Since Proscar contains 5 mg of finasteride per tablet, patients who use Proscar for hair loss typically split the tablet into smaller portions to achieve the appropriate dose. Splitting the pill is cost-effective, as Proscar is often cheaper than Propecia, but care must be taken to ensure accurate dosing.
How Long Should Proscar Be Taken?
Finasteride, whether in the form of Proscar or Propecia, is a long-term treatment for hair loss. Once hair regrowth begins, stopping the medication will likely result in a reversal of its effects. Typically, patients are advised to continue taking Proscar indefinitely to maintain the benefits.
Common Guidelines for Proscar Use in Hair Loss:
- Take the medication at the same time each day, with or without food.
- Consistency is key—missing doses may impact the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor progress and manage any side effects.
Monitoring Hair Regrowth Progress
To track progress, many doctors recommend regular check-ins and photographs to compare hair density over time. Patients are typically encouraged to give the treatment at least 12 months before assessing its full effectiveness.
Side Effects and Risks of Proscar for Hair Loss
While Proscar (finasteride) is highly effective in treating hair loss, it is not without potential side effects. Understanding these risks is crucial for men considering or already using the medication. The side effects of Proscar, although rare, can range from mild to more serious. Moreover, some men may experience side effects that persist even after discontinuing the drug, a condition known as Post-Finasteride Syndrome (PFS).
Common Side Effects
The most frequently reported side effects of Proscar are related to sexual function, as finasteride affects hormonal activity by reducing dihydrotestosterone (DHT). These side effects tend to occur in a small percentage of men and are often reversible once the medication is stopped.
- Decreased Libido (Sex Drive): One of the most commonly reported side effects is a reduction in sexual desire. Men may notice a diminished interest in sexual activity. Studies suggest that about 2-3% of men experience this side effect while on finasteride.
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Some men find it more difficult to achieve or maintain an erection. This side effect may develop within the first few months of taking Proscar and may improve with continued use or after discontinuing the drug.
- Decreased Ejaculatory Volume: Proscar can cause a reduction in the volume of semen during ejaculation, although this does not necessarily affect fertility or the ability to conceive.
- Breast Tenderness or Enlargement (Gynecomastia): A rare side effect of finasteride is the enlargement or tenderness of the breast tissue. Although uncommon, any noticeable breast changes should be brought to the attention of a healthcare provider.
- Depression and Anxiety: Some users have reported mood changes, including feelings of depression, anxiety, and fatigue. These psychological symptoms are relatively uncommon, but they can be distressing when they occur.
Serious Risks
While the common side effects of Proscar are generally mild and reversible, some men may experience more serious risks, particularly with long-term use.
Post-Finasteride Syndrome (PFS):
One of the most concerning risks associated with Proscar is Post-Finasteride Syndrome (PFS). This condition involves persistent sexual, neurological, and physical side effects even after discontinuing the medication. Although the exact cause of PFS is still under investigation, some men have reported continued erectile dysfunction, low libido, depression, and cognitive difficulties for months or years after stopping finasteride.
The risk of PFS is thought to be small, but the severity of symptoms in some cases has led to heightened awareness and research into the syndrome. Men considering Proscar should be aware of this risk and weigh the benefits of treatment against the potential for long-term side effects.
High-Grade Prostate Cancer:
Finasteride has been linked to a slightly increased risk of high-grade prostate cancer. Although finasteride lowers the overall risk of developing prostate cancer by reducing DHT levels, studies have suggested that in rare cases, it may increase the likelihood of more aggressive forms of the disease. Regular monitoring of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) levels is recommended for men taking Proscar, especially those with a family history of prostate cancer.
Allergic Reactions:
As with any medication, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to finasteride, which could include rashes, itching, or swelling. Severe allergic reactions, though rare, require immediate medical attention.
Managing and Mitigating Side Effects
Fortunately, most side effects associated with Proscar are temporary and reversible. Men who experience mild side effects may find that they subside over time as the body adjusts to the medication. However, for those dealing with more serious side effects, it is crucial to take proactive steps:
- Communicate with Your Doctor: Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor for any adverse effects. Your doctor may adjust the dosage or recommend alternative treatments if side effects become problematic.
- Sexual Function and Support: If sexual side effects occur, men should not hesitate to discuss them with their doctor. In some cases, sexual dysfunction can be managed with medications such as PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil) or other therapies designed to improve erectile function.
- Lifestyle Modifications: A healthy lifestyle that includes proper nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management can help minimize the impact of side effects and improve overall well-being. Additionally, reducing alcohol intake and avoiding smoking can benefit both hair health and sexual function.
- Switching to Topical Finasteride: For men who are particularly concerned about side effects, newer formulations of topical finasteride are available. These topical treatments deliver finasteride directly to the scalp, reducing systemic absorption and potentially lowering the risk of sexual side effects.
Patient Stories: Real-Life Experiences with Proscar for Hair Loss
Hearing from men who have used Proscar for hair loss provides valuable insights into both the benefits and challenges of the treatment. Below are a few case studies illustrating a range of experiences, from success stories to those who faced side effects.
Case Study 1: Kevin’s Journey to Hair Regrowth
Kevin, a 32-year-old graphic designer, began noticing hair thinning around his temples and crown in his mid-20s. After trying over-the-counter treatments like minoxidil with minimal results, Kevin decided to consult a dermatologist. He was prescribed Proscar, which he chose due to its affordability compared to Propecia.
“I was nervous about the side effects I had heard about, but after a few months, I started seeing my hair thicken. By the one-year mark, my hairline had filled in noticeably, and I felt a lot more confident. I didn’t experience any side effects, and I’ve been taking it for three years now.”
Kevin continues to take Proscar daily and credits the medication with halting his hair loss. His experience highlights the potential for significant regrowth when Proscar is used consistently over time.
Case Study 2: Mark’s Struggle with Side Effects
Mark, a 41-year-old accountant, began using Proscar after noticing thinning hair on the crown of his head. Within the first six months, Mark noticed a reduction in hair loss and some regrowth. However, he also began experiencing sexual side effects, including a reduced libido and difficulty maintaining an erection.
“I was really excited to see the results with my hair, but the side effects took a toll on my relationship. I eventually decided to stop taking Proscar because the trade-off wasn’t worth it for me. It was a tough decision.”

Mark’s story illustrates the challenge some men face in balancing the benefits of Proscar with its side effects. After stopping the medication, Mark’s hair loss resumed within a few months.
Case Study 3: Jason’s Long-Term Use of Proscar
Jason, a 50-year-old business owner, has been using Proscar for over a decade. He started treatment in his early 40s after noticing hair thinning at the front of his scalp. Jason was initially prescribed Proscar for both hair loss and prostate health, as he also had mild BPH symptoms.
“I’ve been using Proscar for both my hair and prostate issues, and I haven’t experienced any major side effects. My hair hasn’t regrown dramatically, but I’ve maintained most of it, which I’m happy with. The key for me has been sticking with it long-term.”
Jason’s story highlights the importance of consistency when using Proscar. While some men experience dramatic hair regrowth, others like Jason find that the medication works primarily to maintain the hair they have.
Alternative Treatments for Hair Loss and How They Compare to Proscar
While Proscar is one of the most effective medications for treating androgenetic alopecia, it is not the only option available. Several alternative treatments for hair loss exist, each with its own advantages and limitations. Understanding how these treatments compare to Proscar can help men choose the best approach for their specific needs.
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Minoxidil is a topical treatment available over the counter that has been FDA-approved for both men and women. It works by stimulating hair follicles and increasing blood flow to the scalp, promoting hair growth.
- Pros: Minoxidil is easy to use and widely available. It can be applied directly to thinning areas of the scalp, and some men experience noticeable regrowth within a few months.
- Cons: The results of minoxidil are generally less dramatic than finasteride, and it works best when used in combination with other treatments. Additionally, some users experience scalp irritation or dryness.
- Comparison to Proscar: While both minoxidil and Proscar can halt hair loss, Proscar works by addressing the hormonal root cause (DHT), whereas minoxidil stimulates hair follicles directly. Combining the two treatments often yields the best results.
Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplants involve moving hair follicles from a donor area (usually the back of the head) to areas of thinning or baldness. Two primary techniques are used: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
- Pros: Hair transplants provide permanent results and can significantly improve the appearance of the hairline and scalp density.
- Cons: The procedure is expensive and requires a recovery period. The results also depend on the skill of the surgeon and the availability of donor hair.
- Comparison to Proscar: Hair transplants are more invasive and costly than taking Proscar but provide immediate and visible results. However, many men continue to use Proscar after surgery to maintain the health of their non-transplanted hair and prevent further loss.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves drawing a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. The growth factors in the plasma are thought to stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
- Pros: PRP is a non-invasive treatment that uses the body’s natural healing properties to stimulate hair growth. It can be used alongside other treatments like Proscar and minoxidil.
- Cons: The effectiveness of PRP varies from patient to patient, and multiple sessions may be required to see significant results. The cost can also add up over time.
- Comparison to Proscar: PRP therapy is less researched than finasteride and is typically used as a supplementary treatment rather than a standalone solution. It is considered safer for men who want to avoid the systemic side effects of oral medications.
Dutasteride (Avodart)
Dutasteride, like finasteride, is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor. However, it is more potent and inhibits both types of the enzyme that convert testosterone to DHT. Dutasteride is primarily prescribed for BPH but has been used off-label for hair loss.

- Pros: Dutasteride is more effective than finasteride at reducing DHT levels, and some studies suggest it may promote more hair regrowth than Proscar.
- Cons: Because it is more potent, dutasteride may also have a higher risk of side effects, particularly sexual dysfunction. It is not FDA-approved for hair loss, so it must be used off-label.
- Comparison to Proscar: Dutasteride may offer better results for men who do not respond to finasteride. However, due to the increased potency and potential side effects, many men start with finasteride before considering dutasteride.
Lifestyle Changes to Maximize the Effectiveness of Proscar
While Proscar is effective at addressing the hormonal causes of hair loss, certain lifestyle changes can complement its effects and improve overall hair health. These changes can help men maintain their existing hair, support regrowth, and prevent further thinning.
Nutrition for Hair Health
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for healthy hair growth. Key nutrients for hair health include:
- Biotin: Also known as Vitamin B7, biotin is essential for hair growth and can be found in eggs, nuts, and whole grains.
- Zinc: Zinc plays a critical role in hair follicle health, and deficiency can lead to hair thinning. Foods high in zinc include oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds.
- Vitamin D: Low levels of Vitamin D have been linked to hair loss. Sun exposure and foods like fatty fish (salmon, tuna) can help boost Vitamin D levels.
- Iron: Anemia due to low iron levels can contribute to hair loss. Leafy greens, red meat, and lentils are good sources of iron.
Exercise and Scalp Circulation
Regular exercise not only improves overall health but also increases blood circulation, which is vital for delivering nutrients and oxygen to hair follicles. Activities like cardio, yoga, or scalp massage can enhance blood flow to the scalp, potentially improving hair health.
Stress Management
Stress is a well-known contributor to hair loss. Conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair falls out due to stress or trauma, can exacerbate the effects of androgenetic alopecia. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or physical exercise can help minimize hair loss triggered by stress.
Avoiding Hair Loss Triggers
Certain lifestyle habits and grooming practices can exacerbate hair loss. Men using Proscar should take care to avoid:
- Tight Hairstyles: Hairstyles that pull tightly on the hair, such as ponytails, braids, or man buns, can cause traction alopecia, leading to permanent hair loss.
- Heat Styling: Excessive use of heat styling tools like blow dryers or straighteners can damage hair and cause breakage.
- Smoking: Studies have shown that smoking contributes to hair loss by reducing blood flow to the scalp and damaging hair follicles. Quitting smoking can help improve hair health.
The Future of Hair Loss Treatments: Beyond Proscar
As medical research advances, new treatments and technologies for hair loss are being developed, promising even better results with fewer side effects. While Proscar remains one of the most effective treatments currently available, several emerging options may offer alternatives or enhancements to the current approach.
Dutasteride (Avodart)
As mentioned earlier, dutasteride is a more potent 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor than finasteride. While it is not yet FDA-approved for hair loss, ongoing studies suggest it may eventually become a first-line treatment for androgenetic alopecia, particularly for men who do not respond to finasteride.
Topical Finasteride
A newer formulation of topical finasteride has been developed, offering men the benefits of finasteride without the systemic absorption that can lead to side effects. Early studies show promising results in reducing hair loss while minimizing the risk of sexual dysfunction.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is an exciting area of research that aims to stimulate hair follicles and promote regrowth by using the body’s own regenerative cells. Although still in its experimental stages, stem cell therapy holds the potential to revolutionize hair loss treatments by offering a minimally invasive solution with long-lasting effects.
Gene Therapy
In the future, gene therapy may provide a way to reverse hair loss by targeting the genetic factors that cause androgenetic alopecia. By modifying or repairing the genes responsible for hair follicle miniaturization, gene therapy could offer a permanent cure for hair loss.
Hair Cloning
Hair cloning, also known as follicular cell implantation, involves taking a small number of hair follicles, multiplying them in a lab, and implanting them back into the scalp. This technique is still in development but could provide an unlimited source of hair for men with extensive baldness.
Is Proscar the Right Treatment for Hair Loss?
Proscar (finasteride) has proven to be an effective treatment for many men dealing with androgenetic alopecia. Its ability to reduce DHT levels and prevent hair follicle miniaturization makes it a valuable option for those seeking to halt hair loss and potentially regrow hair. However, it is not without risks, particularly the potential for side effects related to sexual function and mental health.
For men considering Proscar, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider to discuss the benefits and risks. Regular monitoring and open communication with a doctor can help mitigate side effects and ensure that the treatment is both safe and effective.
As research continues to evolve, newer treatments like topical finasteride, stem cell therapy, and gene therapy may offer even better solutions in the future. For now, Proscar remains a powerful tool in the fight against hair loss, giving men the opportunity to regain their hair—and their confidence.